
The Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy committee has once again opted to hold the policy rates and stance for the seventh consecutive meeting. The RBI’s approach is rooted in a commitment to bring down inflation, showing that interest rate cuts are contingent upon attaining the inflation target of 4%. Governor Shaktikanta Das said the RBI will prioritise inflation targeting without undermining the growth prospects of the economy.
The vigilance over food price volatility highlights the challenges that could potentially skew the path of inflation targeting. From a phase when retail inflation peaked at 7.8% in April 2022, the RBI’s strategy has evolved from combating rampant inflation to steering it towards a designated target. The MPC’s decision was largely unanimous, except for a solitary dissent favouring a rate cut.
READ I From remittances to robotics: Redefining India’s external sector in a tech-driven world
Economic outlook and policy calibration
The RBI’s prognosis of a 7% growth rate for FY25 is contingent on a fall in headline and core inflation. The volatile crude oil prices and the domestic demand- supply equilibrium in essential commodities like pulses and vegetables are focal points of the central bank’s monitoring regime.
Despite global headwinds, the Indian economy is projected to maintain its strong growth momentum. Leading multilateral institutions such as the World Bank and IMF forecast a GDP growth rate of around 7% for FY25. This optimism is fuelled by several factors, including a slowdown in inflation, robust domestic demand, and continued infrastructure spending by the government. However, challenges remain. Food price volatility and potential disruptions in global supply chains pose risks to the growth trajectory. The RBI’s cautious stance on interest rates reflects this delicate balancing act of fostering growth while managing inflationary pressures.
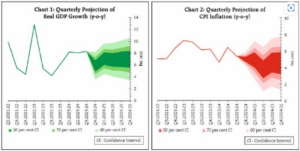
The alignment between India’s fiscal policy and the RBI’s monetary objectives is key to achieving macroeconomic stability. The government’s fiscal prudence, manifested in targeted subsidies and infrastructure spending, complements the central bank’s efforts to control inflation and spur economic growth. This fiscal-monetary synergy is crucial in managing aggregate demand and ensuring that fiscal deficits are conducive to the broader goals of inflation control and economic sustainability.
Sectoral insights and investment climate
The Indian economy, poised for a 7% expansion in FY25, is buoyed by sectoral strengths and favourable monsoon forecasts. The RBI’s growth recalibration for FY25 reflects an understanding of temporal economic fluctuations and growth enablers. The anticipated revival in private sector investment, coupled with government capital expenditure and positive rural demand prospects, promises robust economic activity.
India’s external sector has exhibited remarkable resilience, with a diversification in trade partnerships and a strategic focus on enhancing export competitiveness. The robustness of India’s foreign exchange reserves and the managed float exchange rate regime have provided a cushion against global financial shocks, ensuring external sector stability. India’s trade relations are set to bolster the country’s position in the global trade architecture, enhancing economic resilience and growth prospects.
Urban consumption and investment prospects
The RBI Governor highlighted the vibrancy in urban consumption and the promising indicators bolstering the investment cycle. The synergy of resilient cement and steel sectors, alongside robust capital goods import, underscores the potential for an invigorated investment landscape. The optimism in investment is further reinforced by healthy corporate and bank balance sheets, rising capacity utilisation, and a palpable sense of business optimism.
The digital transformation of the Indian economy is a catalyst for innovation, efficiency, and inclusion. The proliferation of digital infrastructure, fintech, and startup ecosystems has not only democratised financial services but also fostered a conducive environment for technological advancements. This digital revolution is poised to significantly impact monetary policy effectiveness, financial market dynamics, and the broader economic landscape, heralding a new era of economic development and societal progress.
Opportunities and challenges
The global economic outlook is clouded by significant uncertainties. The ongoing war in Ukraine continues to disrupt energy supplies and exacerbate inflationary pressures. Rising interest rates in major economies like the US could trigger capital flight from emerging markets and dampen global trade. The International Monetary Fund has recently downgraded its global growth forecast for 2024 to 3.6%, reflecting these challenges. Despite these headwinds, some bright spots remain. China’s economic reopening offers a potential boost to global trade, and several emerging economies in Asia and Africa are expected to exhibit robust growth.
As India faces global economic uncertainties and domestic challenges, the MPC’s policy stance embodies a strategic equilibrium between growth facilitation and inflation containment. The balance in policy deliberation, reflective of individual and collective economic assessments, charts a course for sustainable growth and macroeconomic stability.
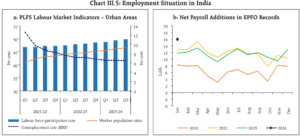
The labour market and the harnessing of India’s demographic dividend are integral to the country’s economic narrative. With a young and increasingly skilled workforce, India is at a critical juncture to capitalise on its demographic potential. The labour market trends, characterised by increasing formalisation and greater female workforce participation, are set to drive consumption patterns and entrepreneurial ventures, fuelling economic growth and enhancing productivity.
The Indian economy stands as a beacon of growth and stability in a tumultuous global economic environment. With strategic policy calibration and vigilant economic stewardship, India is well-positioned to sustain its growth trajectory while managing the domestic and global economic variables. The journey ahead, marked by potential external shocks and domestic economic dynamics, will necessitate astute policy changes to maintain the equilibrium of growth and inflation in Indian economy.
