
The Union Budget 2024-25 presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman has focused on some key areas to bolster the economy. While the budget lays out ambitious plans and promises significant support for the manufacturing sector, there are potential shortcomings and challenges. Here is a look at the budget’s provisions to evaluate their potential impact on the manufacturing sector, highlighting both the promises and the areas where more concrete action is needed to truly benefit the industry.
The manufacturing sector plays a crucial role in job creation, export growth, and overall economic development. The sector has the potential to absorb a large number of workers — critical for India which has a burgeoning population and high unemployment rates. A robust manufacturing base can enhance India’s global trade position by reducing dependence on imports and increasing exports of high-value goods. However, achieving this requires not just policy announcements but effective implementation and addressing deep-rooted challenges such as infrastructure bottlenecks, skill mismatches, and bureaucratic red tape. Here are some key provisions announced for the manufacturing sector.
READ I Union Budget 2024-25: Key takeaways from Nirmala Sitharaman’s speech
The Production Linked Incentive scheme is the cornerstone of the Narendra Modi government’s strategy to boost manufacturing. Budget 2024-25 proposes an expansion of this scheme to additional sectors, including renewable energy components, textiles, and electronics. While the idea is promising, its implementation has faced challenges, including bureaucratic delays and limited awareness among potential beneficiaries. The government needs to streamline processes and ensure that incentives reach the intended recipients without unnecessary hurdles.
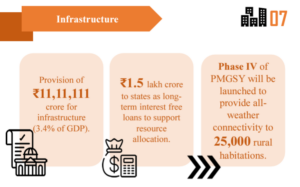
A significant allocation has been made for infrastructure development, with a clear focus on improving transportation networks, power supply, and digital infrastructure. Enhanced infrastructure is vital for reducing the logistics cost for manufacturers and improving supply chain efficiency. Key projects include the expansion of national highways, the development of new industrial corridors, and increased investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
Investment priorities
Call for tax reforms
The budget includes several tax reforms aimed at easing the burden on manufacturers. This includes rationalisation of customs duties on raw materials and intermediaries, which can reduce the cost of production. Furthermore, the introduction of a simplified tax compliance regime is expected to make it easier for businesses to operate and expand. While tax reforms are a positive step, the complexity of India’s tax system remains a significant challenge. Businesses often face issues with tax compliance due to frequent changes in regulations and lack of clarity. The government must focus on creating a stable and predictable tax environment to truly benefit manufacturers.
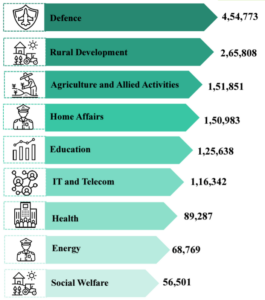
Budget 2024-25: Expenditure on major items
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), which form the backbone of the manufacturing sector, have been given special attention. The budget proposes increased credit support and a new scheme to support technological upgradation in MSMEs. Additionally, there are provisions for addressing delayed payments, a persistent issue faced by MSMEs. The establishment of a dedicated MSME portal for real-time grievance redressal and payment tracking is a notable initiative.
Despite the proposed support, MSMEs continue to struggle with accessing credit and dealing with bureaucratic red tape. The effectiveness of the MSME portal will depend on its usability and the speed of redressal. The government must ensure that these initiatives are not just announcements but are backed by effective execution and monitoring.
Skill development and training
Recognising the need for a skilled workforce, the budget allocates significant resources towards skill development and vocational training programs. The focus is on aligning these programs with industry requirements, particularly in emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, robotics, and advanced manufacturing techniques. The establishment of new centres of excellence in technical education is also on the agenda.
While skill development is crucial, the quality of training programs has often been questioned. There is a gap between the skills imparted and the needs of the industry. The government must work closely with industry stakeholders to design relevant curricula and ensure that training centres have the necessary infrastructure and qualified trainers.
R&D and innovation
To foster innovation and technological advancement, the budget includes increased funding for research and development (R&D) in the manufacturing sector. This includes tax incentives for companies investing in R&D and the establishment of innovation hubs and incubators in collaboration with leading academic institutions.
Despite the increased funding, India’s investment in R&D as a percentage of GDP remains low compared to other major economies. The government needs to create a more conducive environment for private sector investment in R&D. Moreover, the focus should be on not just funding but also on the commercialisation of research outcomes.
Budget 2024-25: Potential impact on manufacturing
The expansion of the PLI scheme is likely to attract both domestic and foreign investment, leading to increased production capacity in various high-tech manufacturing sectors. This can help India integrate more deeply into global supply chains and enhance its export capabilities. Attracting investment is only one part of the equation. The government must also focus on creating a stable policy environment and addressing issues like land acquisition and labour laws to make India a more attractive destination for manufacturing investments.
Rationalising customs duties on raw materials and intermediaries is a strategic move to make Indian manufacturing more competitive. Lower production costs can translate into more competitive pricing for Indian products in the global market, potentially boosting exports. The impact of reduced customs duties may be limited if other costs, such as energy and compliance costs, remain high. A holistic approach to cost reduction is necessary to truly enhance the competitiveness of Indian manufacturing.
Investment in infrastructure, particularly in logistics and power, is expected to significantly enhance the efficiency of manufacturing operations. Improved transportation networks will reduce transit times and costs, while reliable power supply will ensure uninterrupted production processes. Infrastructure development projects often face significant delays. The government must ensure that these projects are completed on time and within budget to realise their intended benefits. Additionally, the focus should be on sustainable and environmentally friendly infrastructure development.
The focus on technological upgradation, especially for MSMEs, is crucial for enhancing productivity and innovation. By adopting advanced technologies, MSMEs can improve their product quality and operational efficiency, making them more competitive both domestically and internationally. Technological upgradation requires significant investment, which many MSMEs may find challenging. The government should provide not just financial support but also technical assistance and training to help MSMEs adopt new technologies effectively.
Challenges and areas of concern
While the budget provisions are promising, the real challenge lies in effective implementation. Delays in infrastructure projects or bureaucratic hurdles in availing tax benefits can dilute the potential positive impact on the manufacturing sector. The government needs to establish robust mechanisms for monitoring and evaluating the implementation of budget provisions. Transparency and accountability in the implementation process are crucial to ensure that the benefits reach the intended recipients.
The manufacturing sector’s performance is closely tied to global economic conditions. Factors such as fluctuating demand, trade tensions, and geopolitical instability can impact the sector’s growth prospects despite supportive domestic policies. The government must develop strategies to mitigate the impact of global economic uncertainties. This includes diversifying export markets, strengthening trade relations, and building resilience in the domestic economy.
Nirmala Sitharaman’s Union Budget 2024-25 has laid down a comprehensive framework to support and boost the manufacturing sector. The expansion of the PLI scheme, infrastructure development, tax reforms, and targeted support for MSMEs are all steps in the right direction. Additionally, the focus on skill development, R&D, and innovation indicates a forward-looking approach to making Indian manufacturing globally competitive.
The success of these measures will largely depend on their timely and effective implementation, along with the ability to navigate global economic challenges. In essence, the budget provides a solid foundation for the manufacturing sector to build upon, but sustained efforts and vigilant monitoring will be necessary to realise its full potential. The manufacturing sector, being a key driver of economic growth and employment, will need continued policy support and strategic initiatives to achieve the desired outcomes and contribute significantly to India’s economic resurgence.
While the budget sets a positive tone, the government must be proactive in addressing potential bottlenecks and challenges. Continuous engagement with industry stakeholders, transparent policy implementation, and a focus on long-term sustainability will be crucial for the manufacturing sector to thrive.
