
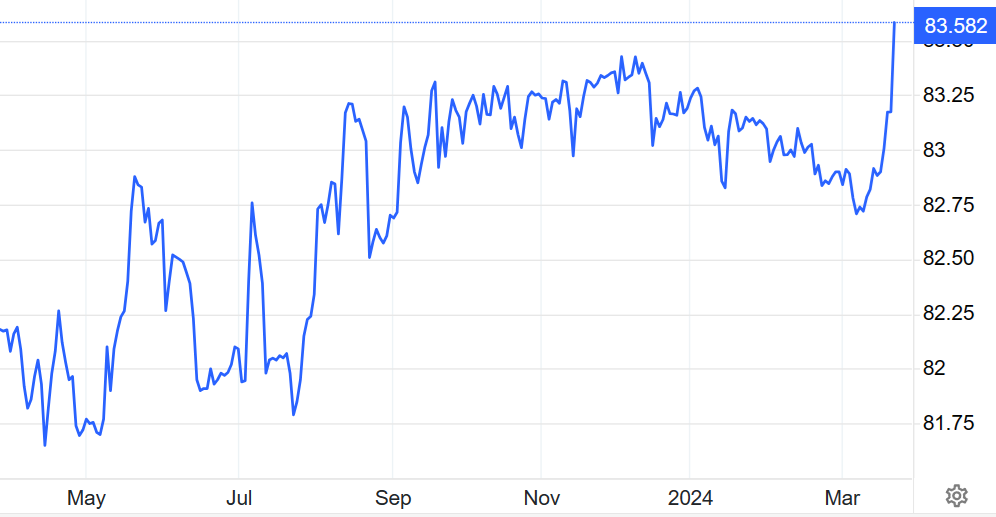
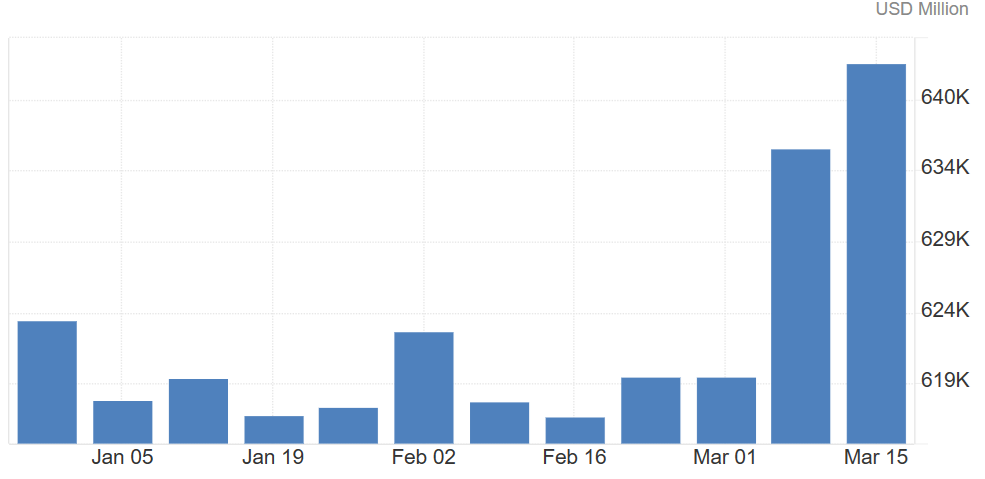
The steady decline of the rupee against the dollar clearly demonstrates the link between domestic policy decisions and global market trends. Despite the depreciation of the currency, India’s foreign exchange reserves have climbed to a record level, signaling the Reserve Bank of India’s effective management in the face of international financial challenges.
The rupee fell to an intra-day low of 83.43, before ending marginally higher at 83.4250, but still down 0.3% from the previous close. The RBI’s choice to not step in during crucial market moments may be aimed at boosting export competitiveness, illustrating India’s recent focus on exports while aligning with wider economic goals.
Rupee decline against dollar continues unabated
India’s economic performance presents a mixed picture. The bright spot is a robust GDP growth rate, projected at 7% for FY 2023-24, surpassing global peers. The dominant services sector, which contributes over 53% of GDP, continues to be a growth engine. However, inflationary pressures remain a concern, with food prices a major contributor. The agricultural sector, a key employer and contributor of around 18% to GDP, faces challenges like inadequate infrastructure and requires modernisation to improve productivity and ensure food security.
The upcoming elections and potential policy shifts add another layer of complexity. This highlights the need for a balanced approach that fosters growth while controlling inflation (currently around 5.9% on average for the past decade) and promoting inclusive development.
READ I Profits vs planet: ESG investing and the need for systemic change
Outlook for rupee vs dollar
Predictions indicate a bright future for the rupee, bolstered by the RBI’s efforts to smooth out extreme market fluctuations. Compared with other emerging market currencies, the rupee’s stability, supported by India’s substantial foreign exchange reserves, reflects a well-controlled currency policy that aligns with the nation’s overall economic trajectory.
However, concerns remain regarding income inequality. While a growing affluent class creates exciting market opportunities, a vast section of the population still grapples with poverty. Bridging this gap is crucial for fostering inclusive and sustainable economic development. The government’s social spending and poverty alleviation schemes will be essential in addressing this challenge.
India’s foreign exchange reserves
India is maintaining a strong GDP growth rate, surpassing its global peers, driven by solid domestic foundations and strategic policy directions. The upcoming Lok Sabha election and its impact on economic policies, particularly through increased subsidies and transfer payments, demonstrate the close connection between political activities and economic planning.
In the business and investment domain, Indian firms are set to increase their investments after the elections, facilitated by strong financials and the strategic shift in manufacturing dependencies. This move from public to private investment highlights the evolving nature of India’s economic growth strategy, where the dynamism of the private sector is expected to play a significant role.
The discussion also touches on the challenges of inflation and the RBI’s careful approach to interest rate adjustments. With persistent inflationary pressures, especially in food prices, the central bank’s cautious stance on rate reductions reflects its commitment to maintaining a balance between fostering growth and controlling inflation.
India’s agricultural sector, a significant employer and contributor to GDP, faces challenges like inadequate infrastructure and volatile weather patterns. Modernisation and investment in agricultural infrastructure are crucial for improving productivity, ensuring food security, and reducing inflationary pressures on essential food items.
The growth in wealth among affluent Indians, reshaping consumer markets and investment trends, adds another dimension to the economic discussion. This rise in affluent consumers points to changing market dynamics and new economic opportunities, indicative of broader shifts within the Indian economy.
Studies on India’s economic situation — currency stability, growth projections, policy strategies, and the rise of affluent consumers — point to an economy poised for steady growth and strategic advancement. As Indian economy faces domestic and global economic adversities, the road ahead presents both challenges and opportunities for sustained growth and resilience. The balanced approach to policy, market, and demographic dynamics offers a detailed view of India’s growth trajectory, marked by strategic planning and a deep understanding of the global economic environment.
