
As the world is reeling under the exponential spread of the Covid-19 pandemic, the World Trade Organisation is busy negotiating a free trade deal in electronic medical equipment. One of the five proposals made to the WTO’s council for trade in goods for combating the pandemic include “removing the impediments to trade in essential products to ensure their free flow”. Other objectives of the Covid-related proposals by 25 countries include: commitment to ensuring supply chain connectivity; predictable trade in agricultural and food; and declaration of trade in essential goods.
While the proposals made by other countries are generic in nature, New Zealand and Singapore have notified a declaration on trade in essential goods for combating the Covid-19 pandemic (“the declaration”) dated April 16, 2020. The joint declaration covers tariff elimination and harmonisation of other import and export measures. It requires any WTO member accepting the declaration to eliminate all customs duties and all other duties, and to refrain from adopting non-tariff barriers, for a list of essential goods provided in two annexes. Annexe I contains124 products belonging to four product groups – medicines, medical supplies, medical equipment and personal protection products. Annexe II has an additional list of 180 products, which are mainly agricultural products. On April 3, 2020, the WTO secretariat had already released a study, which provided an assessment on 96 products, with an intention to liberalise the trade in medical products. This list also includes medical electronics devices and equipment.
READ: ‘COVID-19 lockdown debate is lives vs lives, not lives vs livelihoods’
Thus, the general objective of both the joint declaration and the study appears to be an effort to expand the coverage of the plurilateral sectoral agreements, the Pharma Agreement and the Information Technology Agreement. Plurilateral agreements are agreements negotiated between smaller groups of countries under the WTO.
Trade negotiations are all about timing. These efforts show that the WTO negotiations are not about development and sustainability issues – they are about protecting and promoting the commercial interests of developed countries, as they have always been.
Once again, the current focus is also largely on tariff elimination. The two proponents, Singapore and New Zealand that have called for free trade in these essential goods, together do not account for more than 3% share in total global medical equipment imports. Further, with Singapore’s MFN duties at 0% and New Zealand’s average applied MFN duty on medical equipments at 0.8%, tariff elimination does not stand to disrupt their domestic producers. Developed countries mostly depend on domestic regulations and standards to regulate imports.
READ: Screening FDI: Need of the hour in the time of non-transparent capital flows
Unfortunately, tariffs (ad-valorem) remain the prominent barrier for imports into developing countries. For instance, India’s average applied MFN duty for medical equipment stands at about 9%. Increasing import competition at a time of economic distress from the national lockdown will be at the loss of our domestic producer firms of medical equipment. Thus, bringing down the tariff duty just serves the producer firms from developed countries to have greater access to our markets. The usage of domestic regulations and standards, which would have addressed the concerns in the absence of tariffs, is sparse across the developing world.
During the emergency caused by the pandemic, the WTO may have a role to act on the removal of supply chain disruptions in essential medical (and agricultural) goods. However, the elimination of tariffs is the least of its immediate concerns. Importing countries with higher duties on medical products (and high import requirements during this period) can unilaterally decide to bring them down temporarily, factoring in the concerns of their domestic industry. On the contrary, there is a need to address the concerns of SME exporters from developing countries which include higher industry standards in the developed countries and compliance with third-party certification requirements. The route adopted presently only highlights the agenda of the developed world.
READ: Lessons for India from global manufacturing hubs
India was a willing participant to the first Information Technology Agreement (ITA-1) eliminating tariffs on 217 IT products. This was concluded between 82 members representing about 97% of world trade in IT products. At the Nairobi Ministerial Conference in December 2015, over 50 members concluded the expansion of the agreement, which now covers an additional 201 products valued at over $1.3 trillion per year. Having learned its lessons from the disastrous impact of the ITA-1 on the domestic IT hardware manufacturing producers, India did not become a party to the ITA-expansion agreement.
The possibility of a medical goods agreement would mean the merging of two plurilaterals – the Pharma Agreement and the ITA-expansion agreement, as it covers 11% products under the ITA-expansion agreement. The other dimension to the present medical goods proposal is that it has products that were also present in the NAMA healthcare sector sectoral proposal of 2008. The declaration list covers 25% of the products in the NAMA sectoral. Both of these clearly point towards the beginning of the expanding coverage for trade liberalisation targeted at large markets like India.
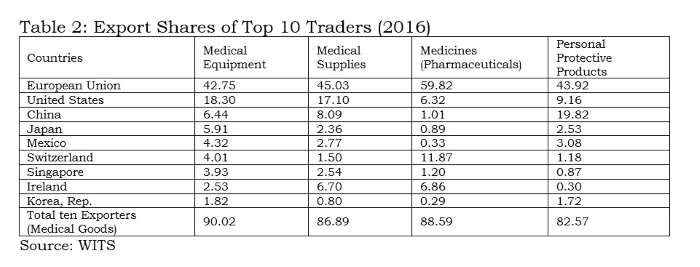
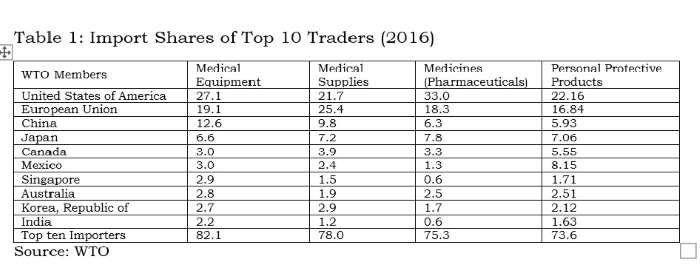
Tables 1 and 2 clearly indicate the process of facilitation done by the WTO for a few countries. Any liberalisation by participating countries under the declaration would facilitate countries like the EU, US, China, Japan, Mexico, Switzerland, Singapore, Ireland and Korea, which accounted for 90% of global exports in medical equipment. Among these, China is the only developing country with supplying capacities; and it is well known that the value addition by MNCs in Chinese manufacturing is rather low.
India does import 2.2% of medical equipment, but its export share is only 0.5%; therefore, it would not be wise for India to join this declaration. Similar to the 1996 plurilateral (ITA-1), reduction of tariffs without domestic-oriented technical regulations and standards will virtually wipe out the production capacities in developing countries like India in medical equipment.
The above tables also indicate the pattern of very high demand and supply between USA, EU, China, Japan, Canada, Mexico, Singapore and South Korea. Rather than proposing any agreement on medical goods, these countries should have bilateral deals.
READ: Foolproof PDS: A practical guide to food security
The suppliers (firms) that have benefitted from tariff-only trade liberalisation carried out under the WTO so far have mostly been from the developed world which offer products meeting the regulatory standards made by the International Standards Organisation (ISO) or private industrial bodies or associations. With these product standards being tweaked by the lead firm/industrial association/exporting country, all WTO negotiations are purely commercial deals. In the absence of appropriate disciplining of non-tariff measures at the global level, countries like the EU, Switzerland, Japan and the US will be allowed a free run in supplying about 71% of the global medical equipment market. All 135 products under the medical goods (combined list of products from the WTO study and the declaration) are essential. However, for India, electronics and medical products are both strategic sectors. Therefore, taking on the onus of further tariff-only liberalisation under any proposal at the WTO, without national industry-specific standards, will not serve India’s strategic interests.
The developed members are attempting to play the old tricks, which some of them have mastered over more than seven decades of international trade negotiations. This is a reminder to the South that even in a pandemic, the North is only bothered about consolidating the market shares of their firms. The developing and less developed countries have to guard against old ways creeping into the emerging world trade rules. This calls for an urgent need to reform the organisation to get rid of data gaps and information asymmetry.
(Murali Kallummal is Professor, Centre for WTO Studies, IIFT and Smitha Francis is Consultant, Institute for Studies in Industrial Development.)
Murali Kallummal is Professor, Centre for WTO Studies, CRIT, IIFT, New Delhi. Views are personal.

