
Last month, scientists at the Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam made a startling discovery – microplastics were detected in the blood samples of 80% of the people tested for research. While plastic particles have earlier been detected in fish and other sea organisms, this was the first time that they were detected in human blood. The study showed that these particles may move freely around the body and lodge themselves in any of the organs. While its impact on health is yet to be ascertained, researchers are worried these particles could result in millions of early deaths every year.
The latest developments in plastics research offer hope. Researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have developed an enzyme that can break down plastic in 24 hours, offering a way to tackle the plastic waste crisis, say media reports. The scientists used artificial intelligence to produce an enzyme named hydrolase which can break down polyethylene terephthalate or PET, a common kind of plastic which comprises more than 12% of the solid waste in the world.
READ I UNEA agreement on plastic pollution a landmark
A solution to plastic pollution
Apart from tackling the waste problem, this enzyme could also help companies recycle their products, helping create a circular plastics economy, according to a paper titled ‘Machine learning-aided engineering of hydrolases for PET depolymerization’, published last week in peer-reviewed journal Nature.
The earlier efforts to break down plastics using enzymes were not as successful because such chemicals are vulnerable in certain pH ranges and temperatures. The new enzyme does not have this drawback. The researchers claim that the enzyme could clean up landfills and dumping sites when used in ample quantities.
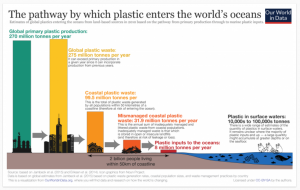
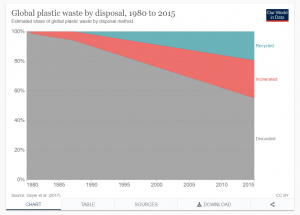
The world produces at least 400 million tonnes of plastic waste a year. Annual plastic production is expected to touch 1,100 million tonnes by 2050. More than a third of the global plastic output is used for packaging. Around 85% of this ends up in landfills and a large quantity ends up in water bodies. More than 8 million tonnes of plastic waste enter the oceans every year. The waste breaks down into microplastic particles and enter living organisms through food, water and air.
In a landmark development in March, 175 United Nations members agreed to sign a global agreement to tackle plastic pollution. The treaty is expected to tackle excess supply of plastics which are produced primarily by the hydrocarbon industry.
