
The global electric vehicle market is experiencing a transformative surge, but a new challenge has emerged for established carmakers worldwide: China’s dominant position. With superior technology, affordability, and a supportive government, Chinese EV manufacturers are rapidly capturing market share, leaving Western and Asian auto giants scrambling to adapt. This shift in dynamics underscores the complex interplay between technological advancements, market trends, and evolving consumer preferences, all within the context of a rapidly evolving global electric vehicle market.
Superior performance, affordability, and a large domestic market are the factors behind the success of Chinese products. Electric car sales in China surpassed 7.7 million units in 2023, representing a staggering 36% surge from the previous year. In contrast, the US market, the second largest, is experiencing relatively lower growth rates, with sales touching 1.5 million units.
READ | Success of India’s millets drive hinges on policy push
EV push in China
One crucial factor contributing to the disparity between Chinese and American markets is the preference for larger vehicles among US consumers. This preference necessitates more expensive batteries, increasing the cost of EVs and hindering widespread adoption. Additionally, concerns such as ‘range anxiety’ further impede sales in the US, as many drivers are reluctant to embrace electric vehicles without extended driving ranges on a single charge.
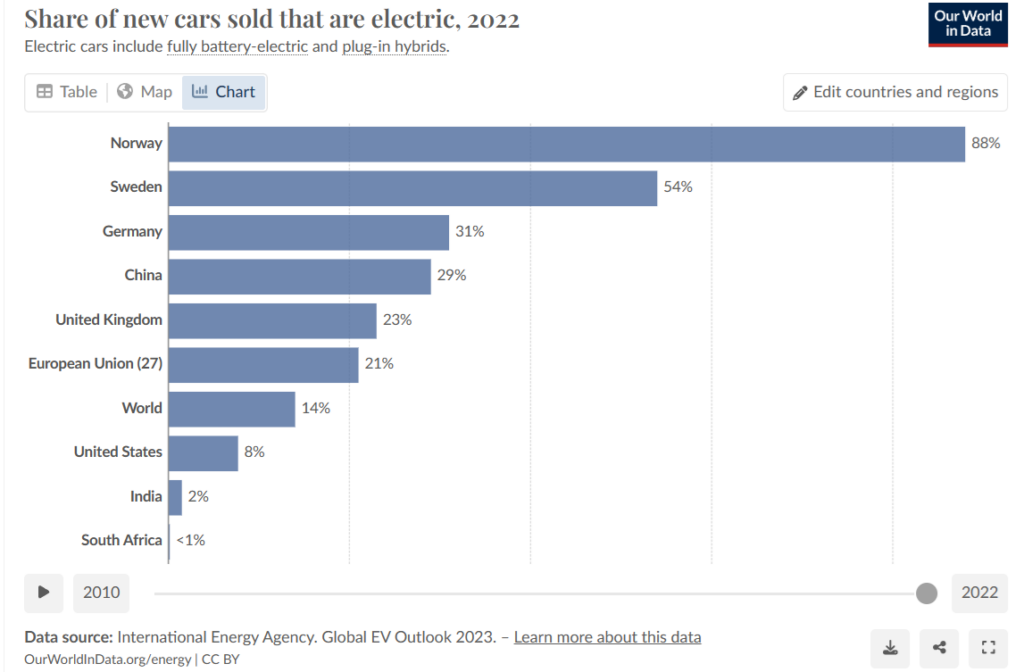
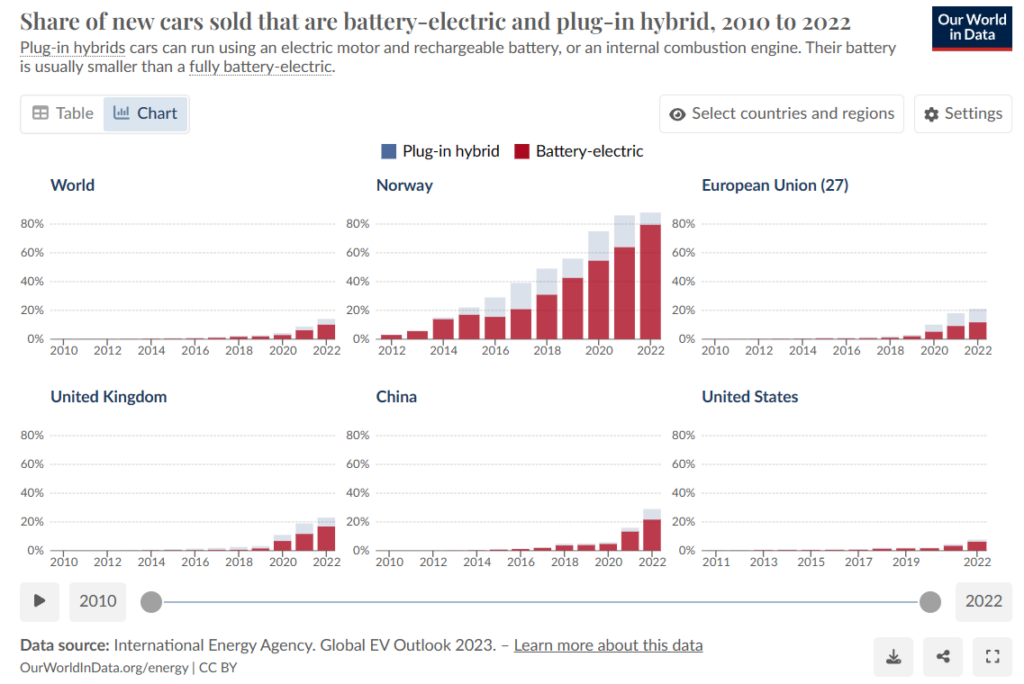
Overall, the global EV market continues to experience rapid growth and evolution, driven by technological advancements, regulatory incentives, and shifting consumer preferences. While China leads in the production and adoption of electric vehicles, other regions like Europe and India are also witnessing significant momentum in electric mobility. With EV sales soaring across the world, and the potential emergence of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles as competitors, the automotive industry stands on the brink of a sustainable transportation revolution.
Across the world, sale of battery driven cars has surged, albeit at varying rates. In Europe, countries like Norway lead the charge in adoption, with electric vehicles accounting for over 70% of new car sales in recent years. European automakers, spurred by stringent emissions regulations and government incentives, are ramping up production to meet growing consumer demand. Similarly, countries like India are witnessing a burgeoning interest in electric mobility, fuelled by government initiatives and rising environmental consciousness among consumers.
Infrastructure and environmental challenges
An aspect often overlooked in comparing EV markets is the state of charging infrastructure and its consequential impact on consumer adoption rates. Chinese manufacturers have excelled in production and innovation, complemented by substantial investments in charging networks. This infrastructure readiness has significantly driven adoption in China. Conversely, the United States lags behind in developing a comprehensive charging infrastructure network, posing a significant hurdle for US carmakers and contributing to sluggish sale of electric vehicles in the US.
Apart from performance and affordability, environmental considerations also shape consumer preferences in the EV market. Chinese manufacturers capitalise on this by emphasising sustainability and eco-friendliness in their offerings. This eco-conscious approach resonates strongly with consumers globally, contributing to the success of Chinese vehicles. In contrast, US carmakers have been slower to prioritise environmental concerns, potentially impacting their market appeal.
Government incentives, innovations
The success of EVs is intricately linked to government policies, incentives, and technological innovations. China’s dominance can be attributed, in part, to its robust regulatory framework and generous subsidies for EV buyers, incentivising consumers to transition to electric mobility. Conversely, the United States grapples with fragmented policies and inconsistent incentives, impeding widespread adoption. Addressing regulatory barriers and implementing cohesive policies will be essential to accelerating adoption in the US.
Technological innovations also play a pivotal role in driving the market’s evolution. Chinese manufacturers leverage technologies like solid-state batteries and advanced driver-assistance systems to enhance performance and appeal. These advancements address critical concerns such as range anxiety and safety. In contrast, US carmakers have been slower to embrace cutting-edge technologies, potentially limiting their competitiveness.
Strategic adjustments and industry challenges
Strategic adjustments by major players, like Hertz divesting a portion of its EV fleet, highlight the complexities of the market. Despite efforts such as new model launches and price reductions, the anticipated surge in demand has not materialised, prompting companies to reassess their strategies and priorities.
Moreover, challenges extend beyond automakers to companies producing essential battery components. Despite significant revenue growth, companies like Rivian Automotive report substantial losses, reflecting broader market challenges. Apple’s decision to discontinue its car project highlights the uncertainties of the market and the growing emphasis on AI-driven technologies.
Amid the rise of EVs, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have emerged as potential rivals to battery-powered EVs. FCVs use hydrogen gas to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct, offering a clean alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. While FCVs have yet to achieve widespread adoption, advancements in hydrogen infrastructure and production technologies could propel their growth in the coming years. In countries like Japan and South Korea, where hydrogen infrastructure is more developed, FCVs have garnered attention as viable alternatives to conventional vehicles.
However, challenges remain for the widespread adoption of FCVs, including limited hydrogen refuelling infrastructure, higher production costs, and technological hurdles. Battery powered vehicles currently enjoy a significant market advantage, benefitting from a more established infrastructure and lower manufacturing costs. Nonetheless, as research and development in hydrogen technology continue to progress, FCVs could emerge as formidable competitors to battery powered vehcles in the global automotive market.
China’s rise in the market is exemplified by BYD overtaking Tesla as the world’s largest EV manufacturer. BYD’s success underscores China’s conducive regulatory environment, strong government support, and proactive domestic automakers. As China continues to lead in production and innovation, it poses challenges for global competitors, prompting concerns about trade barriers and tariffs.
The future of the electric vehicle market will be shaped by technological advancements, regulatory developments, and shifting consumer preferences. While challenges persist, opportunities for growth and innovation remain as stakeholders adapt to the evolving landscape of electric mobility. Leveraging emerging technologies and adopting a flexible approach to market dynamics will be crucial for industry players to unlock the full potential of electric vehicles and pave the way for a sustainable future of transportation.
